Chapter 4 Genetics the Science of Heredity Review Science Answers
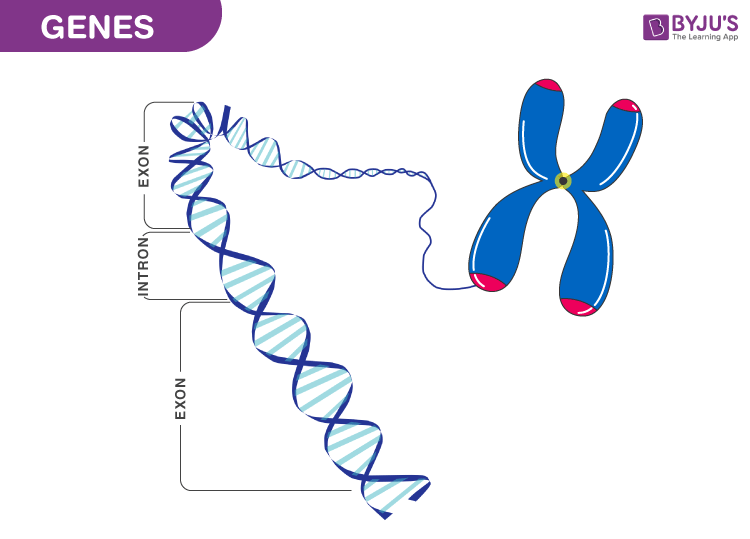
Genetics is a branch of the biological science involved with the study heredity, its biological procedure, the written report of genes, genome, jail cell cycle, heredity, inherits genes and lot more.
What is Genetics?
The exploration of the working and major codes of variation and heredity is termed as Genetics. The background on which heredity stands is known as inheritance. It is divers every bit the procedure by which characteristics are handed downwardly from one generation to the other. Gregor Johann Mendel is known as the "Father of Modernistic Genetics" for his discoveries on the basic principles of heredity.
Variation, as the name suggests is the corporeality of dissimilarity that exists in between children and their parentages. Information technology can be adamant to keep in view the behaviouristic, cytological, physiological, and morphological characters of individuals plumbing equipment into similar species.
Some of the major reasons that variation are
- Genetic/Chromosomal rearrangement.
- Mutated genes due to the influence of the ecosystem.
- Crossing over.
Let us take a detailed look at genetics notes to learn near genes and the principle of inheritance.
Law of Inheritance by Gregor Mendel
Garden Pea (Pisum Sativum) was the plant that Mendel experimented on for 7 years to become to the signal to propose the laws of inheritance in live creatures. Mendel carefully chose seven distinct characteristics of Pisum Sativum for the investigation concerning hybridization. Mendel used truthful-breeding lines i.e. those that go through constant self-pollination and display steady feature bequest.
Also Read: Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Principles of Inheritance
When Mendel observed the monohybrid cross he proposed two laws of inheritance-
Police force of Authorisation – Distinct elements termed as factors control the characteristics. These factors at all times exist as a couple. One of the constituent genes of the couple dominates over the former.
Law of Segregation – Alleles don't alloy and the two characteristics are recuperated all through the gamete germination (in the F2 generation). The characters apart from each other and pass on to diverse gametes. Comparable types of gametes are produced by Homozygous and heterozygous produces diverse sorts of a gamete with varied characteristics.
Also Refer: Principles of Heredity
Incomplete Dominance
It is the discovery that was done after Mendel's work. Incomplete authorization is the situation in which both the alleles do not display a dominant trait resulting in a fine combination or a midway amid the characteristics of the alleles.
Explore more: Incomplete authorization
Codominance
When two alleles lack the dominant-recessive association and thus the duo affects the fauna together.
Constabulary of Independent Assortment
Separation of one set of the feature is autonomous of the other set of the characters when they are pooled in a hybrid.
The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
Both genes and chromosomes exist in sets of two. The homologous chromosome contains the two alleles of a gene pair in the homologous sites. The coupling and split of a set up of chromosomes volition cause a split in the gear up of genes (factor) they carry. This united knowledge is termed as the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance.
Sex Conclusion
A particular nuclear system was perceived by Henking. He perceived that this particular nuclear arrangement was found in simply fifty per cent of sperms. He termed this body as x. Later it became clear that just Ovum's that obtain only the x chromosome is born female and those that don't have such a case are born male. Thus, the X- chromosome was termed every bit sex activity chromosome and the remaining ones were termed equally autosomes.
The occurrence due to which a modification in Deoxyribonucleic acid happens and causes a variation in the phenotype and genotype of a brute is termed every bit a Mutation.
Explore more than:Decision Of Sex
Genetic Disorders
Disorders of a Mendelian nature include:
- Haemophilia.
- Sickle Cell Anaemia.
- Phenylketonuria.
Disorders of a chromosomal nature include:
- Down's syndrome.
- Klinefelter'south Syndrome.
- Turners Syndrome.
Explore more: Chromosomal Abnormalities
Learn more than in detail about Genetics, its importance, applications and other related topics @ Byju's Biology
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/genetics/
0 Response to "Chapter 4 Genetics the Science of Heredity Review Science Answers"
Post a Comment